FeaturesBranch Management
Pushing and Fetching
Configure Git authentication methods in GitButler for pushing and fetching from remote repositories using SSH, Git executable, or credential helpers.
GitButler can authenticate with an upstream Git server in several different ways.
You can just tell us to use the system Git executable, which you can setup however you want. You can use our built in SSH protocol with your own SSH key (this does not require you to have Git installed), or you can use the default Git credentials helper.
You can set your preference (and test if it works) in your project's "Git authentication" section:
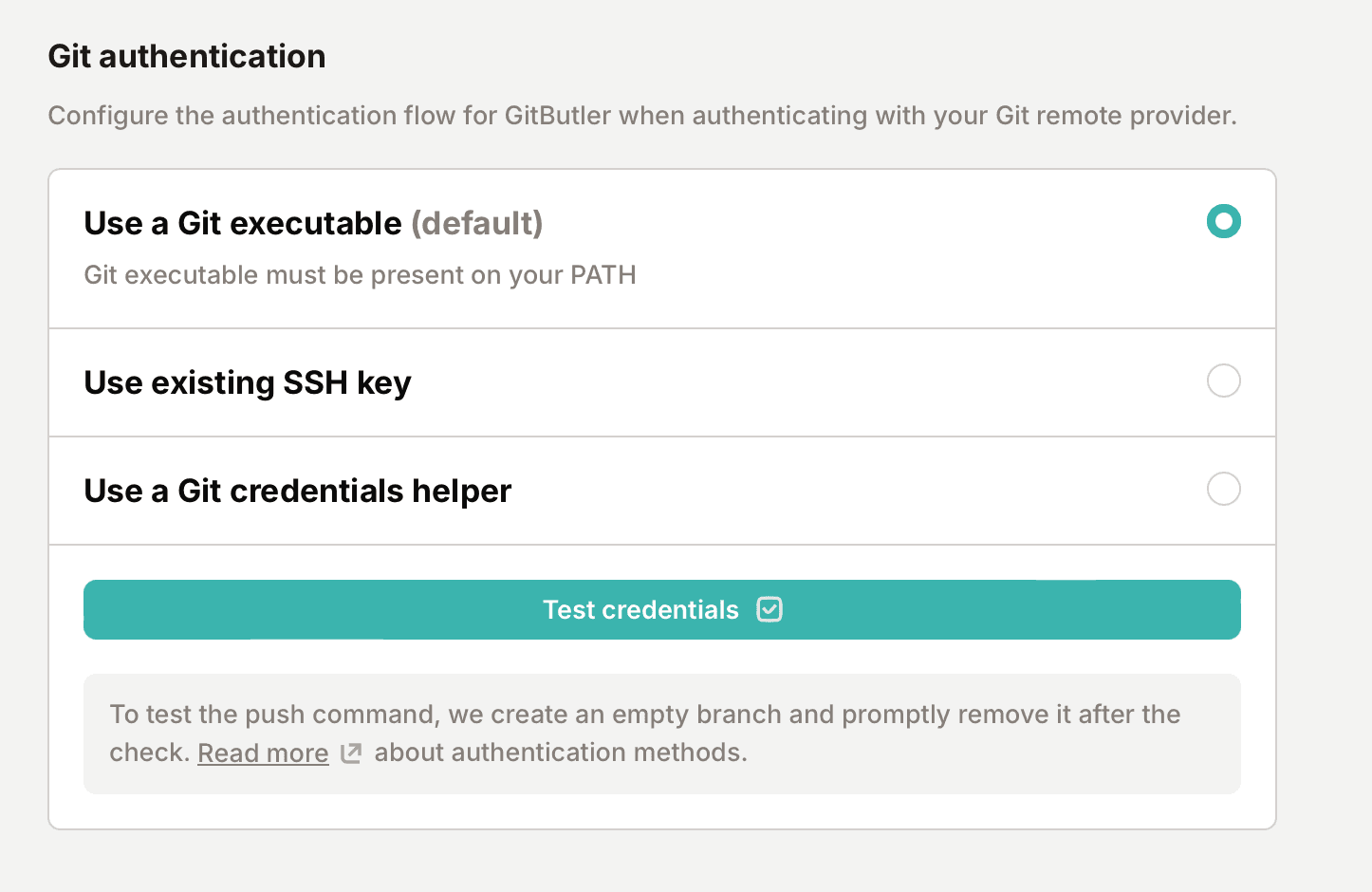
Once that's done, GitButler will be able to automatically fetch upstream work and push new branches to your upstream server.
Last updated on